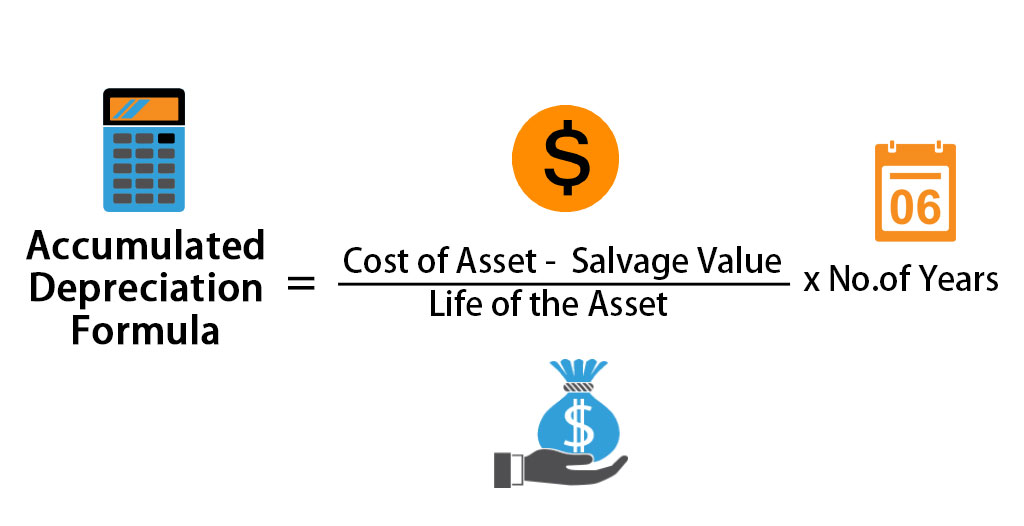

When depreciation already appears in trial balance, it means journal entry is already made and asset account has been already reduced to the extent of depreciation. Hence, depreciation will be shown only in profit and loss account. At the beginning of the next accounting period, the above entry is reversed to bring into account accrued income at the beginning, so that it is reduced from amount of income in the next year. When a company prepays for an expense, it is recognized as a prepaid asset on the balance sheet and it reduces the company’s cash by the same amount. The prepaid expense is deducted from the particular expense while preparing a profit and loss statement. An accrued expense is an expense incurred, but currently not recorded in the account books.
A journal entry is typically made as an automatic reversed entry, which means that accounting software generates an offset entry at the start of the next month. After that, when the vendor ultimately submits an invoice to the business, it erases that reversed record. Let’s understand the double accrued interest journal entry entry system with the help of an example. An organization purchases equipment by paying for it in cash. Now, in this, the transaction affects two accounts, which is, equipment account and cash account. As the equipment is purchased, it increases for the business, in turn, cash decreases.
Khatabook Blogs are meant purely for educational discussion of financial products and services. Khatabook does not make a guarantee that the service will meet your requirements, or that it will be uninterrupted, timely and secure, and that errors, if any, will be corrected. The material and information contained herein is for general information purposes only. Consult a professional before relying on the information to make any legal, financial or business decisions.
Another benefit is that the financial statement readers can view all the obligations and potential due dates. For instance, the financial statement will display the entire scope of transactions than the cash accounting. To ensure that your financial reports appear accurate according to the accrual-based basis in accounting, an accountant needs to create an adjusting entry at the end of December.
Whereas, in recurring deposits, the customer deposits fixed amounts in small intervals for a long period. Fixed Deposit is asset by nature therefore Fixed deposit is shown in the Asset side of balance sheet . Ltd. makes no warranties or representations, express or implied, on products offered through the platform.
The general ledger is the foremost essential of financial reporting. It is used to prepare various financial statements like the income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and so on. The purpose of giving such commission may be to motivate the managers to work with their full potential, to reward the managers for their efficiency and to retain the efficient managers by rewarding them sufficiently. Such commission can be calculated only at the end of the accounting period after calculating net profit. Hence, it remains outstanding at the end of the accounting period.
So, the chances of causing errors or discrepancies are virtually none. You can use the accrued expense journals to record every transaction, making its data easily accessible. The same can be reversed easily by bank branch by debiting the interest income account and crediting the related advance account .
(vii) Interest on drawings
Hence, the income received in advance account will be shown only in the liabilities side of balance sheet. No adjustment is necessary in income account as already it would have been adjusted. If accrued income account appears in the trial balance with debit balance, it means that journal entry has been made already for accrued income.
Since the transaction was completely omitted from the books, the normal journal entry for accrued interest will be passed. However, this method will have the same effect on the Profit and Loss Account of whole bank as that of in the above method mentioned in para 6.3. In both the method the current year’s profit / loss of the entire bank will get affected by the unrealized interest of preceding years. Therefore, this method may involve duplicate work at both branch and Head Office level. The unrealized interest remains of two types i.e., unrealized interest pertaining to the current year and the unrealized interest pertaining to the preceding years.
Hence, the outstanding expenses account will be shown only in the liabilities side of balance sheet. No adjustment is therefore necessary in expenses account as already expenses would have been adjusted. The subject matter discussed on prepaid expenses, accrued income and income received in advance is one of the core studies for accounts. A good grasp on the matter is beneficial as the expenses and the incomes together form a business transaction and a financial event to take place accordingly.
Is accrued interest a debit or credit?
The amount of accrued interest for the recipient of the payment is a debit to the interest receivable (asset) account and a credit to the interest revenue account. The debit is rolled into the balance sheet (as a short-term asset) and the credit into the income statement.
According to the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles , expenses should be recorded in the same accounting period as the benefit generated from the related asset. For example, a company uses leased machinery for twelve months, the company benefits from it over a full-time period. Recording an advanced payment made for the lease as an expense in the first month would not adequately match expenses with revenues generated from its use.
Accrued Expenses Journal Entry Example
Therefore, it should be recorded as a prepaid expense and allocated out to expense over the full twelve months. Prepaid expenses represent prepayment of an expense and hence it is debited and the cash account is credited. This records the prepayment as an asset on the company’s balance sheet, such as prepaid insurance and debits an expense account on the income statement, such as insurance expense.
What is the journal entry for accrued interest?
An accrued interest journal entry is a method of recording the amount of interest on a loan that has already occurred but is yet to be paid by the borrower and yet to be received by the lender. Accrued interest is the interest gained on outstanding debts over a particular financial period.
Of course all this requires change in rules, policies and standards in respect of banks by appropriate govt. It is a general accounting concept that an amount in any account can be reversed only if the same has been credited in that account in the current year and is also laying there at the time of passing the reversal entry. Here the amount intended to be reversed has never been credited to the current year’s interest income account (as the same was credited to the preceding years’ income accounts). If outstanding expenses account appears in the trial balance with credit balance, it means that journal entry has been made already for outstanding expenses.
Income Tax Filing
However, the company can debit the account and add this as an expense line to lessen the impact. A large number of expenses could significantly impact the income statement. Paying off its outstanding accounts payable at the end of the year reduces accrued costs.
This concept in accounting is known as double-entry bookkeeping. Business entities may have investments in outside securities carrying specified rate of interest. If interest is due but not yet received, adjustment is to be made for the same in the accounting records before preparation of final accounts. Interest receivable on any investments in the form of shares, deposits, etc. made outside the business is called accrued interest.
Provision for bad and doubtful debts refers to amount set aside as a charge against profit to meet any loss arising due to bad debt in future. At the end of the accounting period, there may be certain debts which are doubtful, i.e., the amount to be received from debtors may or may not be received. In some cases, the yet to be earned revenue belonging to a future accounting period is received in the current accounting period, then such income is considered as the ‘income received in advance’. This income is also called the Unearned Revenue, Unearned Income, Income Received but not Earned these names are because it is received before the related benefits that are being provided.
One Rank One Pension (OROP) revision arrears before 15th March 2023 (in one go): PCDA(P) Circular 667
To reflect this in the financial statements, it will require an adjustment entry in the account books. Interest expense is the cost incurred by an entity in connection with the borrowing of funds which may include loans, bonds or other forms of credit for business purpose or for the acquisition of asset. It is a non-operating expense shown on the income statement representing interest accrued during the period covered by the financial statements and not by the amount of interest paid during the period. The information in this article describes the accrued expenses’ significance and meaning in extremely easy terms.
- At the beginning of the next accounting period this entry is reversed to bring into account the opening stock.
- Provision for discount on debtors is made on the basis of past experience at an estimated rate on sundry debtors.
- When goods are given as Charity, it results in an outflow of the goods purchased.
- To reflect this in the financial statements, it will require an adjustment entry in the account books.
This is because provision for discount is to be expected only on good book debts. When the amount realisable itself is doubtful, provision for discount is not to be made. Similar to bad debts and provision for doubtful debts, here also discount allowed to debtors must be transferred to provision for discount on debtors account if a provision exists. Provision for discount on debtors is made on the basis of past experience at an estimated rate on sundry debtors. Discount should be calculated on sundry debtors after deducting bad debts and provision for bad debts.
To bring into account income accrued and received in advance. To record omissions in trial balance such as closing stock, interest on capital, interest on drawings, etc. Interest expense is usually charged to the statement of profit and loss. However, if certain conditions specified for capitalization as per AS 16 Borrowing Costs are met then such interest expense should be capitalized to cost of the related asset. This kind of accounting journal entry employs a double-entry technique which means you could debit one account and credit another. This improves the accuracy of your accounting system and makes audits much easier.
Accrued Income is the income that is earned but not yet received. ‘Income received in advance, as the name suggests, is the earned revenue which is to be earned in the future in an accounting period but is already received in the current accounting period. Interest expense is a line item on a company’s income statement indicating the amount that has been incurred by an entity on the funds borrowed. Interest recorded in the Income Statement represents the interest accrued during the period covered by the financial statements; not the amount of interest paid over that period. Interest income, on the other hand, is the revenue earned by an entity for lending their funds or letting others to use entity’s resources. Both these items are separate line item in company’s financial statement and therefore, should be disclosed separately for each period.
How do you record accrued interest in accounting?
To record the accrued interest over an accounting period, debit your Interest Expense account and credit your Accrued Interest Payable account. This increases your expense and payable accounts.
It accepts no liability for any damages or losses, however caused, in connection with the use of, or on the reliance of its product or related services. Accrued utilities are a great example of using utility services for your business but have not paid yet. One is that an accrued cost is not backed by an invoice from a supplier, unlike an account payable, which is backed by a vendor invoice.
How do you record accrued interest in accounting?
To record the accrued interest over an accounting period, debit your Interest Expense account and credit your Accrued Interest Payable account. This increases your expense and payable accounts.
